When worn correctly, both Bluetooth and wired earbuds offer a lightweight and comfortable way to listen…
How To Block Radiation: Key Steps You Can Take Now

*We may earn a commission for purchases made using our links. Please see our disclosure to learn more.
In our modern society, we are constantly bombarded with radiation. Some sources are natural, such as from the sun. Other sources, such as your WiFi signal, are not. Either way, it is clear that co-existing with radiation exposure is simply a part of life these days.
If that doesn’t sit well with you, you’re not alone. But unfortunately, eliminating all of the potential nearby sources of radiation in your home is not exactly realistic. And even then, you can only control so much. There are many external sources that you will be unable to eliminate completely. Blocking radiation, on the other hand, is a much more doable solution.
So how do you block radiation? Read on to find out.
Radiation 101
The approach necessary to block radiation depends on the type of radiation in question. What does that mean?
Well, as it turns out, the term radiation is actually quite broad. There are several different forms, all of which can be found at different frequency ranges on the electromagnetic spectrum.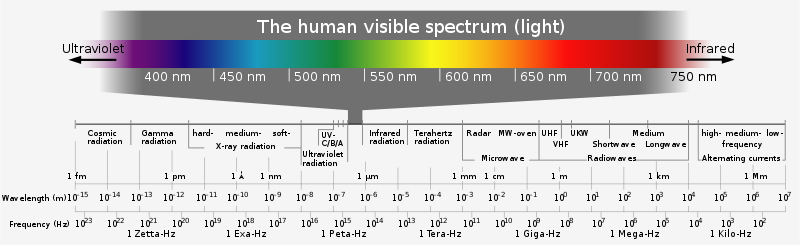
Think of the human visible light spectrum as the dividing point between the two primary categories of radiation: ionizing and non-ionizing. Ionizing radiation refers to the frequencies to the left of the visible spectrum in the above image, starting with ultraviolet light, while non-ionizing encompasses those to the right, starting with infrared light.
Types of ionizing radiation include x-rays, gamma rays, and cosmic background radiation. This type of radiation consists of tightly wound waves that contain enough energy to force an electron out of its orbit.
Types of non-ionizing radiation, meanwhile, include radio waves, microwaves, and extremely low-frequency waves. Non-ionizing radiation does not have as much energy as its ionizing counterpart. The waves are more spaced out, and they lack the necessary energy to cause direct changes to an atom’s electrons.
As you can see, the two different categories of radiation have different properties due to their energy levels. Therefore, what works to block one may not work against the other.
For our purposes today, that’s all you really need to know about the types of radiation. If you’re curious to learn more, however, we cover this topic in much greater depth in EMF Radiation: Everything You Need To Know.
Blocking ionizing radiation
In general, ionizing radiation can be blocked by any material that is dense enough to prevent the waves from passing through. The density required varies depending on the type of ionizing wave — for an alpha ray, for example, a piece of paper is sufficient enough to stop the wave in its tracks. But for x-rays, a much thicker material such as lead is required.
Let’s take a look at a few of the more common types of ionizing radiation and what, if anything, you can do to block them.
Ultraviolet light
There is a tendency to use sunlight and UV rays interchangeably. In reality, however, this is misleading. Only a small percentage — between eight and ten percent — of sunlight falls within the ultraviolet frequency range (which is roughly between 30PHz and 750THz). The rest of the rays consist of infrared light as well as a large percentage — about 42% — that falls within the visible light spectrum.
Ultraviolet light may not make up the bulk of sunlight, but it is still the primary culprit behind the development of conditions such as sunburns and skin cancer. So protecting from UV rays is pretty important.
Fortunately, there are many easy ways to do this. To block ultraviolet waves from your skin, you can apply a high SPF sunscreen. Try to aim for something 50 SPF or higher, and be sure to apply regularly throughout the day, particularly if you find yourself going swimming or sweating a lot.
Another way to block ultraviolet light is through the use of a sun guard. Sun guards cover up most of your visible skin, and some even have cooling properties to help prevent overheating while wearing them. One great sun guard for women is BALEAF’s Women’s Long Sleeve Half-Zip Sun Protection Rashguard. A similar option for men exists, as well, with Hanes Men’s Long Sleeve Cool Dri T-Shirt, which acts as a 50+ SPF buffer between you and the sun.
X-Rays and other forms of ionizing radiation
As we mentioned earlier, many of these other forms of ionizing radiation are best blocked by an extremely dense metal such as lead. Think about when you go to your dentist for a cleaning and they take those x-rays of your mouth. At that moment, you are asked to put on a lead vest and sometimes even a thyroid caller to keep your exposure levels to a minimum.
So yes, dense materials can indeed be effective against ionizing radiation. That being said, unless you are in a profession where you’re required to be next to an ionizing radiation source, you may not need to invest in any ionizing radioprotection on its own. It’s not impossible to block, but our daily exposure is so minimal that there may be no point. And generally, when we are exposed in a medical or professional setting, we are provided with the necessary items to keep us safe.
Blocking non-ionizing radiation
Non-ionizing radiation, meanwhile, is a bit of a different beast. This type of radiation is tricky because its low waves can easily penetrate through a material that ionizing radiation cannot. With EMFs and other types of non-ionizing radiation, then, a better rule of thumb is to search for conductive metals.
Let’s now take a look at some of the more common types of non-ionizing EMF radiation and how to block them.
5G
There are actually three different types of 5G: low band, mid-band, and high band. The low and mid bands operate very similarly to your standard 4G radiation, which we will discuss under “cell phones” below. In this section, we are exclusively interested in how to block high-band (or “millimeter wave” 5G radiation, which operates between 24GHz and 39GHz.
To effectively attenuate a high-band 5G signal, it requires a material capable of deflecting or absorbing those particular wavelengths. Many standard EMF protective products are not really designed to tackle frequencies that high, but there are a few out there that are up to the challenge. Take, for example, DefenderShield’s EMF Radiation Protection Blanket.
According to the manufacturer, this blanket is capable of shielding the wearer from up to 99% of nearby RF radiation, including 5G frequencies. This blanket is the perfect accompaniment for anyone who frequently uses their phone or laptop near their body, or even keeping an expectant mother’s belly protected from nearby radiation.
To learn more about 5G radiation, see our collection of 5G articles here.
Smart meters
Smart meters are massive producers of RF-EMF radiation, due to the signal they transmit to and from your utility company. This radiation blasts from the device in all directions, meaning it likely increases the EMF levels in your yard as well as around the interior wall on the other side of the meter.
One way to reduce the amount of radiation produced is to use a smart meter cover. If you’re familiar with the concept of a Faraday cage, these work in much the same way. They are made from a conductive metal mesh that prevents radiation from exiting, while still allowing the meter’s transmissions to pass through. One excellent cover is from Smart Meter Guard. Their mesh covering fastens securely over your meter’s glass and reduces the unit’s EMF output by up to 98%.
We discuss smart meter radiation in greater depth here.
Cell phones
By now, you are probably well aware of cell phone radiation. These devices produce RF-EMF radiation when they are powered on and connected to the network, and for most of us, our phones are pretty much constantly in that state. Of course, you can always put the device in airplane mode to significantly reduce its EMF output, but that affects your phone’s functionality and isn’t always a practical solution if you need to be easily reachable or do something that requires an internet connection.
One thing you can do to keep yourself safe as you stay connected is to invest in an EMF protective case. SafeSleeve’s Anti Radiation Cell Phone Case comes in multiple different sizes to fit a variety of phones. It has also been lab-tested to verify its effectiveness and can block up to 99% of your phone’s EMF emissions. Granted, the case doesn’t help you when you are actively using the phone, but it’s quite useful when you’re on the go or simply need to leave your phone powered on and nearby.
If you’d like to learn more about cell phone radiation, how it works, and how to stay protected, see our in-depth guide: “Cell Phone Radiation Protection: Everything You Need To Know.”
WiFi
Another common culprit of EMF radiation in your home is the WiFi signal. When your wireless router broadcasts its signal, it is actually sending out radio frequency waves — in other words, RF-EMF radiation. Normally, we would recommend switching from wireless to wired internet, to completely eliminate this as a radiation source.
If that is not feasible, however, you can block some of the radiation by installing a WiFi router guard. JJ Care’s WiFi Router Cover is a metal mesh cage, very similar to the smart meter cover we talked about above. Your router goes into the cage, and the wires can slide through a small hole. This enclosure prevents about 95% of your router’s EMF radiation from exiting the cage.
To learn more about WiFi radiation and how to stay protected, see our guide here.
Parting thoughts
How to block radiation depends largely on the type of radiation you’re trying to block. Whether it’s UV light or EMF radiation, there are many products out there that make blocking radiation easier.



